When Is the Best Time to Go Fishing?

Timing is everything when it comes to fishing, and knowing when to cast your line can turn a good day on the water into a great one. Whether you're a seasoned pro or an angling newbie, knowing when the best time to go fishing is can make all the difference. Let’s dive into the times fish are most likely to bite so you can reel in a big one every time.
Key Takeaways
- Best Time to Go Fishing — The best time to go fishing varies by the fish species you’re targeting and your location, but dawn and dusk in spring and fall are generally considered prime fishing times.
- What Weather Do Fish Bite Best in? — Fish tend to bite best on days that are overcast or have light to moderate rain.
- What Time of Day Do You Catch the Most Fish? — You’re more likely to catch fish near dawn and dusk when fish are actively feeding.
- Tools & Resources for Finding the Best Time to Fish — Anglers can use fishing apps, websites, online forums, lunar tables, and almanacs to find the best time to go fishing in their area.
- When Not to Fish — Fishing is less successful after heavy rain and cold fronts and during periods of extreme temperatures, clear skies, strong winds, full daylight, and neap tides.
Best Time to Go Fishing
Although the best times to go fishing can vary by fish species and geographic location, there are a few general seasonal guidelines you can follow. We’ve summarized them below:
| Best Time to Go Fishing by Season | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Spring | Summer | Fall | Winter |
|
Fish Species |
Largemouth bass, smallmouth bass, trout, walleye, crappie, northern pike, perch, catfish |
Largemouth bass, catfish, bluegill, salmon, carp |
Smallmouth bass, trout, walleye, crappie, striped bass, northern pike, redfish (red drum), muskellunge (muskie), catfish |
Redfish (red drum), flounder, yellow perch, crappie, pickerel, catfish |
|
Time of Day |
Dawn and dusk |
Dawn and dusk |
Dawn and dusk |
Midday |
|
Fish Activity Level |
High |
Moderate |
High |
Low to moderate |
|
Ideal Fishing Locations |
Freshwater lakes, rivers, sallow waters, near rocky areas, submerged structures |
Lakes, ponds, coastal areas, deeper waters, near vegetation, river mouths |
Rivers, lakes, coastal areas, near rocky shorelines, weed edges, tidal waters |
Ice fishing spots, coastal areas, deeper holes, sandy bottoms |
|
Water Column Positon* |
Mid to shallow |
Mid to deep |
Mid to shallow |
Deep |
|
Seasonal Fishing Tips |
Use live bait fish near vegetation |
Fish in deeper water and use sun protection |
Focus on shallow waters and use brightly colored lures |
Dress warmly, fish slowly, and use small bait |
*The water column position is the depth at which a fish is located or where you are targeting fish in the water body.
In spring, as water temperatures start to rise, fish become more active and begin feeding aggressively to prepare for spawning. This makes them easier to find and catch. Bass, trout, and walleye are particularly active during spring.
In the fall, water temperatures begin to cool, and fish feed heavily to prepare for winter. Because summer activities have ended, waterways tend to be less crowded, making it easier to attract fish. Species like pike and musky are especially easy to catch with lures in the fall.
“Best times to fish are in spring and fall in freshwater, and during fall for
saltwater. Dusk and dawn are always the best times to get out there as well.
You’ll get massive topwater blowups especially at dawn. Remember, if you’re
comfortable, the fish probably are too, and that means they’ll be out patrolling
for baitfish.”
- Adam Cunningham, Fishing Category Marketing Specialist –
Academy Sports + Outdoors
Spawning Season Considerations & Regulations
Spawning season — the time of year when fish reproduce — is crucial for maintaining healthy populations. Many regions implement restrictions, such as catch-and-release-only policies or complete no-fishing periods, to protect them.
Anglers should always stay informed about local regulations and practice responsible fishing habits during these periods, such as avoiding nesting areas and handling any accidentally caught spawning fish with extra care before releasing them back into the water.
Regulations can typically be found on state wildlife or natural resource agency websites. Some regions also have apps dedicated to providing up-to-date information.

What Weather Do Fish Bite Best in?
Overcast skies are ideal for fishing. When it’s cloudy, fish are more likely to venture out from their cover to feed because the dimmer light reduces their visibility to predators and prey. This is especially true for light-sensitive fish species like bass.
Overcast days bring barometric pressure (the force exerted by the weight of the air in the Earth's atmosphere) changes associated with approaching storms, which cause fish to feed more aggressively in anticipation of changing weather.
Light to moderately rainy days break up water surfaces, which can mask the presence of anglers and their gear. Rain also washes insects and other bait into the water, naturally stirring fish to feed. However, during heavy rains, fish might become more difficult to catch because of the environmental change it causes.
Why Fish Don’t Bite After it Rains
Rain can cause runoff to enter into bodies of water, leading to muddied conditions. Many fish rely on sight to locate their prey, and murky water can reduce their ability to see lures or bait. Runoff can also affect water oxygen levels and pH balance, making fish lethargic and less likely to bite.
Rain can cause sudden drops in water temperature that can temporarily shock fish and reduce their activity levels. It also leads to higher water levels, which allow fish to explore new areas. With more areas to hide and hunt, fish might not be as concentrated or interested in baits and lures.

What Time of Day Do You Catch the Most Fish?
The best times of day to catch fish are around dawn and dusk. During sunrise and sunset, the sun is low on the horizon, creating dimmer light conditions. Many fish are more active during these times because the reduced light provides better cover from predators. They have evolved to take advantage of these conditions.
The reduced light also changes the water temperature. Fish are sensitive to these subtle shifts in temperature, which can trigger feeding activity. Many smaller prey, like insects and baitfish, are more active during these cooler parts of the day as well, attracting bigger, predatory fish.
Turnover in Lakes & Rivers
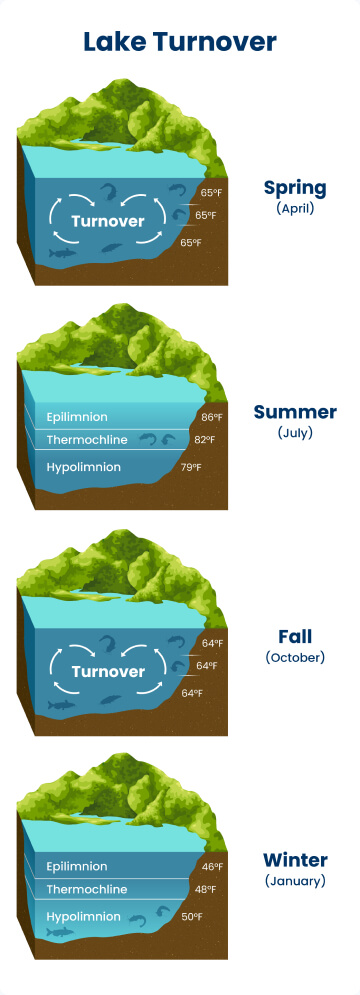
Lake turnover is a natural process that happens in lakes during the spring and fall. During the summer, lakes have layers with warm water on top and cold water at the bottom. In the fall, the surface water cools down, becomes denser, and sinks, causing the lake's water to mix. This process reverses in the spring.
While rivers don't have a turnover process like lakes, their water levels can mix during seasonal changes. This is usually caused by increased water flow from rainfall or melting snow, which stirs up sediments and nutrients.
Turnover helps distribute oxygen throughout the lake, making fish more active and spread out. It also mixes nutrients from the bottom of the water with the other layers, attracting fish to different feeding areas. These conditions make it easier to locate fish, as many species will migrate to areas with higher oxygen levels.
How the Moon & Tides Affect Fishing

The moon and tides are mainly relevant to saltwater fishing. The moon's gravitational pull controls the ocean's tides. When it causes the water level to rise, it’s known as high tide. When it causes water levels to decrease, it’s known as low tide.
High tides can bring saltwater fish closer to shore and into estuaries, making them more accessible to shore-based anglers. Low tides restrict fish to deeper channels and holes where they might be more concentrated but also more cautious due to the reduced depth.
The moon's phases also affect the strength and timing of tides. Full and new moons create what are known as ‘spring tides,’ characterized by higher high tides and lower low tides. These tides lead to more fish activity because fish adjust their feeding habits to exploit new feeding grounds exposed by the shifting waters.
During the quarter phases of the moon, neap tides occur. These are milder tides with less extreme differences between high and low tides, resulting in potentially less fish activity.

Tools & Resources for Finding the Best Time to Fish
Knowing the best times to go fishing is great, but tracking these changing conditions can be difficult. Thankfully, there are plenty of resources out there to help you.
Fishing Apps
In this day and age, you likely have access to a smartphone — use it to your advantage! Check out these popular fishing apps and bring your newfound knowledge with you on your next trip:
- Fishbrain: Offers local fishing maps, forecasts, and social networking with other anglers.
- Fishidy: Provides detailed fishing maps with marked fishing spots and real-time fishing reports.
- Navionics: Excellent for charting and mapping water bodies, which is particularly useful for boaters.
Websites & Online Forums
If apps aren’t you’re thing, there are websites that offer similar information. Before grabbing your gear, explore these fishing websites:
- Tides4Fishing: Offers detailed tide charts, solunar tables, and weather forecasts for coastal anglers.
- TakeMeFishing.org: Provides fishing forecasts, tips, and regional fishing regulation information.
- NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration): Provides comprehensive weather updates and marine forecasts.
- Online Forums: Joining an online forum or fishing club can give you access to the collective knowledge and experiences of seasoned anglers in your area.
Almanacs & Lunar Tables
Unfortunately, most calendars don’t include moon phases or peak local fishing times. However, this information can be found in the following resources:
- The Old Farmer’s Almanac: Includes fishing calendars based on solunar theories.
- Solunarforecast.com: Gives the best fishing times based on your location and moon phases.

When Not to Fish
The old saying, “If the cows are laying down, the fish aren’t biting,” may not be accurate, but it does hold some truth. Fish sense and react to changes in atmospheric (or barometric) pressure, meaning different weather conditions may be better for fishing than others. Fishing is generally unsuccessful during:
- Heavy Rain or Storms: Poor visibility and high water can make fishing challenging and less productive.
- Extreme Temperatures: Fish may become lethargic and less active, staying in deeper, more stable waters.
- Clear Skies: Fish may feel more pressure in higher barometric conditions (days with clear skies), making them less likely to feed.
- Strong Winds: Can stir up sediment in the water, reducing visibility and making it difficult for fish to find bait.
- Full Daylight: Bright sunlight can make fish wary and drive them to deeper waters or cover.
- Neap Tides: Less water movement during quarter moon phases can decrease fish activity because food and nutrients are less stirred up.
- After Cold Fronts: Fish often go into a dormant state and feed less aggressively after the passing of a cold front due to the sudden drop in temperatures.
- Peak Fishing Times at Popular Spots: An overabundance of fishing activity in one area can make fish more cautious and reduce your likelihood of success.
- After a Full Moon or New Moon: Fish are generally resting up from their increased activity the night before.
Have Fun Out There!
Knowing the best time to go fishing is the key to reeling in some impressive catches. So, grab your gear, keep an eye on the skies, and head out when the fish are likely to be biting! If you’re ready to gear up for your next adventure, check out the selection of fishing gear and equipment available at Academy Sports + Outdoors.